What is gum treatment?
The gum treatment, also known as periodontology, is a branch of science that studies prevention, diagnose and treatment of the gum diseases. The conditions affecting gum and bone tissue which cause inflammation accordingly are defined as periodontal diseases. An early diagnosis of the periodontal diseases plays a fundamental role in treating the dental and oral health problems easily and successfully and maintaining long term dental health.
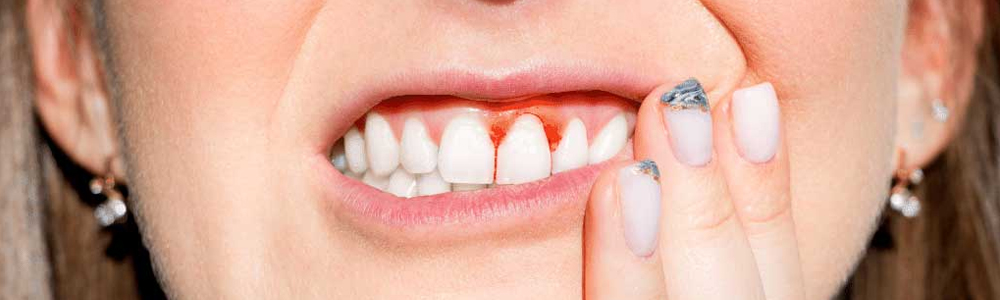
Healthy gums are pale pink and have firm and matte surface. They almost never bleed during brushing. Bleeding gums are the most significant symptom of dental disease. Even though there is no other kind of dental issue, bleeding gums eventually can lead to teeth loss on its own.
What are Common Gum Diseases?
Gum diseases which require dental treatment become visible gradually. Early stage of gum disease is the inflammation of gums which also known as “gingivitis”. Untreated gum diseases can damage the tissues that anchor the teeth on jaw and the inflammation grows more severe accordingly. These severe and serious gum diseases are called “periodontitis”. Periodontitis is a serious gum disease and should be treated rapidly. Generally speaking, gum diseases don’t have easily noticeable symptoms. So, taking precautions and regular dental visits are a very important for avoiding gum diseases.
What are the symptoms of gum diseases ?
- Bleeding gums spontaneously or when flossing,
- Redness, swelling and irregularity of the gums,
- Mild pain when pressing the gums, inflammation of the gums and/or tooth sensitivity in that area,
- Gum recession and sensitivity of exposed root surfaces,
- Black areas on the edges of the gums caused by tartar stones,
- Teeth wobble, lengthen and open up between teeth,
- The feeling of change in your bite when you close your mouth,
- Smell and bad taste in the mouth due to inflammation,
- Itching sensation (in the gums).
WHAT CAUSES GUM DISEASES ?
- Bacterial plaque,
- Smoking,
- Genetic factors,
- Hormonal changes,
- Stress,
- Drug use ( If you are using birth control pills, antidepressants and heart medication drugs, please tell your dentist),
- Tooth clamping or scraping,
- Diabetes,
- Bad nutrition ,
- Poorly made bridges and crown filling.
VARIETY OF DENTAL DISEASES:
- GINGIVITIS This is the simplest form of gum disease. It causes the gums to become red and swollen. The gums bleed quickly. Usually the patient does not feel much discomfort at this stage. With professional treatment and good care, gum health can be restored. If your oral care habits are insufficient, gingivitis begins to develop into periodontitis,
- AGGRESSIVE PERIODONTITIS With this type, at first sight, it seems that there is no problem. But on the contrary, the disease progresses in an aggressive and destructive way. It may not respond to gum treatment and require antimicrobial (antibiotic) treatment,
- CHRONIC PERIODONTITIS, Due to inflammation of the supporting tissues of the tooth, there is progressive attachment (the tissue between the tooth and the gum) and bone loss. It is characteristic with pockets and receding gums. It is the most common type of periodontitis. Although it is mostly seen in adults, it can be seen at any age. The loss of attachment is usually slow, but periods of rapid advancement can also occur,
- PERIODONTITIS AS AN INDICATOR OF SYSTEMIC DISEASE, It is most commonly seen in young people with systemic disease such as diabetes,
- NECROTISING PERIODONTITIS, There is necrotising inflammation of the alveolar bone (bone tissue surrounding the tooth), the periodontal ligament (fibres between the tooth and the bone) and the gum tissue. It is seen more frequently in people with a weakened immune system, malnutrition.
HOW GUM DISEASE IS TREATED
Teeth Scalling / Cleaning Tartar : Even if you take the necessary care of your teeth, it is inevitable to have bacteria in your mouth. This may lead to the formation of calculus over time. Tartar is a problem that can cause serious tooth and gum problems if the necessary precautions are not taken. Detertrage, that is, dental calculus cleaning performed by specialist physicians, helps to protect your oral health and smile.
Dental Curettage :
What is a Periodontal Curettage?
Curette treatment is a cleaning operation of the damaged tooth and periodontal pockets to avoid dental diseases. It has a remarkable effect on removing the subgingival bacteria and plague. Periodontal curettage is mistaken for tooth scaling frequently. While tooth scaling is the removal of plague bacteria from surface of the tooth, curettage treatment goes below the gum line to clean the bacteria proceeded to the root.
Why would someone need periodontal curettage?
Bleeding, swollen or reddened gums are the most common complaints of the patients to whom periodontal curettage is applied. Late diagnose of these symptoms make periodontal curettage essential instead of traditional tooth scaling. A dental checkup once in six months plays significant role in preventing gingival diseases.
Advantages of Curettage Treatment
Like any other dental treatments, the purpose of curettage treatment is to maintain oral and dental health. Prevention of gum disease can be achieved by applying curettage treatment before it gets more compelling. Cleaning the oral bacteria prevents other kinds of dental illnesses and health problems that can result from bad oral health. By protecting jawbone health, problems like bone loss and tooth loss can be avoided.
How To Do Periodontal Curettage?
Curettage treatment is a procedure usually performed under local anesthesia. The very first step after injection of local anesthetic is inserting a sharp dental instrument through periodontal pockets to remove the inflamed soft tissue and clean bacteria. The same procedure is carried out on every tooth and pocket until the cleaning is thoroughly completed and a deep dental cleaning is acquired. Patients should frequently flush their mouth with a sterile solution to sweep out the discarded bacteria. At the end of the operation, gum is smoothed so that they do not provide a surface for bacteria and tartar.
Flap Dental Surgery
What is a Flap Dental Surgery?
Flap dental surgery is an operation during which the gums are surgically separated from teeth with temporal a flap-like incision to have access to the root and the bone more easily. The dental pockets provide an ideal environment for harmful bacteria and create holes which are almost impossible to be cleaned. Oral bacteria cause infection after a certain time and the complaints such as tooth sensitivity, bleeding and aching issues emerge. Flap dental surgery helps eliminating these complaints.
How To Perform Flap Dental Surgery?
Flap dental surgery can be performed under local anesthesia. Giving relaxant syrup and anxiety drugs to patient during anesthesia is another option. After anesthesia, the very first thing to do is making a tiny incision to separate tooth and the gum. The gum is folded back on the purpose of reaching tooth root, ligaments and bone tissue easily.
After completing this procedure, the first objective of the surgery is fulfilled and infected gum is scraped. The gum causing discomfort is excised, bacteria is removed completely and the root is deeply cleansed. If any damage is detected on the bone tissue, dental graft is used to repair the damage.
On the final phase, after the proper dental interventions are conducted completely, the operation is ended by closing the incision. When performed by a specialist in the field, flap dental surgery is a treatment with a high success rate.
- CROWN LENGTH EXTENSION OPERATION This is a simple procedure to lengthen the parts of the teeth (parts visible in the mouth) above the gum line. In some cases, decay or fracture progresses below the gum line or the length of the teeth is very short. In such cases, it is necessary to extend the gum level towards the root for retention of prosthetic treatments (crown, bridge, etc.) and gum health.
- GINGIVECTOMY AND GINGIVOPLASTY In some cases, inflammatory, drug-related or hereditary gingival enlargements are observed. If these gingival growths are not accompanied by bone resorption or if there are no deep defects requiring bone formation, the gingival growths can be removed by cutting the soft tissue wall of the pocket between the tooth and the gum. This procedure is called a gingivectomy. After this procedure, the gingivoplasty procedure is usually applied to restore normal appearance by surgically correcting the gum,
TISSUE GRAFTING
Soft tissue grafting: This is the process of covering obvious gum recessions that occur in one or more teeth due to misuse of the toothbrush, anatomical errors or gum disease, with soft tissue fragments taken from another part of the mouth (usually the palate). It is usually performed for cosmetic purposes or, in some cases, for preventive purposes to prevent gum disease from progressing.
Hard tissue grafts: Bone formation is stimulated by applications of artificial or natural bone powder in areas of advanced bone loss during flap operations.
WHAT TO DO TO HAVE HEALTY TEETH ?
- Brush your teeth properly and floss daily,
- Eat a balanced diet, avoid empty calories and very sticky foods,
- Learn to examine yourself and do so regularly. This way you can pick up the early signals of any oral changes.
- Visit the dentist at least twice a year for check-ups and tartar removal.
